
HRM LEVEL
1. HRMs' Concerns regarding the financial performance of human capital
The following elements show that HRMs do not doubt that it is their responsibility to facilitate the processing of non-GAAP reporting data impacting the financial performance of the firm's HR assets.
Recent surveys (ABV Group - Willis Towers Watson 2019 and Gartner 2019) have revealed the intention of HR Managers to meet the challenge of real-time integration of HR-Finance processes:
. 69% reported that the variable portion of compensation and performance pay is levers for improving the effectiveness of remuneration and for 91% of HRMs, cost control remains an imperative.
. For HRMs key ERM indicators that drive the HR function include:
. Annual performance review (86%),
. Employee commitment (81%),
. Payroll (76%),
. Training (70%),
. Compensation competitiveness (65%) and
. Cost of absenteeism (60%).
2. Exercises to be done on the Fintech HR application module (IT-IRM) of your workstation by referring to the seminar and tutorials of your modules (Free access during training)
Use the access code to your Fintech HR platform (IT-IRM) that you received when registering for this exercise.
2-1/ HR Function's survey for Employee Satisfaction and Commitment:
a) Carry out surveys of anticipation of the deterioration of the social situation to provide motivation data and mobilization of employees.
b) Apply the integration of enterprise learning to manage turnover and have knowledge gap data to identify hiring requirements.
c) Use the internal dashboard to monitor and support the improvement of employees' financial performance and purchasing power indexed on five socio-economic indicators that are levers on which each employee can act in real time.
d) Use the internal dashboard to take immediate and effective action to address risk based on six key domains of socioeconomic improvement:
- Working conditions
- Organization of work
- Consultation, communication, coordination (3C)
- Integrated training
- Working time management and
- Strategic implementation.
2-2/ HR Function's survey for psychosocial risk measurement:
Use the access code to your Fintech HR platform (IT-IRM) that you received when registering for this exercise.
Conducting periodic surveys of “Psychosocial Risks” to provide alert data on HR dashboards based on six axes:
a) Work requirements
b) Emotional requirements
c) Autonomy
d) Margins of maneuver
e) Social and labor relations
f) Different value conflicts.

OM LEVEL
Use the access code to your Fintech HR platform (IT-IRM) that you received when registering for this exercise.
Exercises for the coordination of the work of the operational units heads to be done on the Fintech HR application module (IT-IRM) of your workstation (Free access during training):
A/Organize operational units and coordinating the capture of daily incidents related to indicators, factors or causes of operational risk losses.
B/ Avoid the mistake which until now has consisted in focusing employees on the socioeconomic indicator of greatest concern.
C/ Explain, referring to the seminar and tutorial guide for the modules of your workstation, the protocol for collecting incident data and mitigating operational risk losses related to socio-economic indicators within the reach of each employee to improve his financial performance and his variable salary.
D/The following are five indicators, whose daily data collected by the heads of business units or CGUs dashboards, are articulated and weighted to manage the financial performance of HR in real time:
a) Absenteeism loss mitigation reporting accounts;
b) Work accident loss mitigation reporting accounts;
c) Quality deficiency loss mitigation reporting accounts;
d) Reporting accounts for mitigation of loss of direct productivity gaps (overtime and overconsumption of materials);
e) Reporting accounts for mitigation of loss of know-how gaps (including lack of versatility).

OPERATIONAL UNITS HEADS LEVEL
Use the access code to your Fintech HR platform (IT-IRM) that you received when registering for this exercise.
Exercises to be done on the Fintech HR application module (IT-IRM) of your workstation (Free access during training):
A/ Maintain and update the list of team members.
B/ Explain to the members of the team, referring to the tutorial of the module, the keeping for each employee of the daily data recording sheets of the five socio-economic indicators below, factors or causes of operational risk losses:
a) Absenteeism loss mitigation reporting accounts;
b) Work accident loss mitigation reporting accounts;
c) Quality deficiency loss mitigation reporting accounts;
d) Reporting accounts for mitigation of loss of direct productivity gaps (overtime and overconsumption of materials);
e) Reporting accounts for mitigation of loss of know-how gaps (including lack of versatility).
C/ Explain, referring to the seminar how, operating structurally, each indicator driving the others, the five indicators are taken together in the weighting system transferred by the HRM module to that of the CFO for planning and reporting internal financial performance.
D/ Learn how to enter the financial performance indicators data of the employee’s team on weekly fact sheets;
E/Interact with the Human Resources (HR) department to mobilize employees in the line of business and the team to participate in periodic surveys to measure employee satisfaction and psychosocial risks;
F/ Organize the periodic interviews of operational unit heads and employees. This is done with each unit to monitor, evaluate and propose strategies to improve the financial performance of each unit, assess variable salaries, and index purchasing power on five socio-economic indicators.
.These indicators are levers on which each employee can act in real time.
G/Process of the Employee Financial Performance Recognition eBulletin indexed to socio-economic indicators: Weekly entry of data to be processed to pay variable wages on five socio-economic indicators of financial performance mitigating operational risk losses based on the risk appetite threshold.
H/Train operational unit employees to download, reading and assess their Performance e-Bulletins.
E/ Explain, referring to the seminar how, operating structurally, each indicator driving the others, the five indicators are taken together in the weighting system transferred by the HRM module to that of the CFO for planning and reporting internal financial performance.

CFO LEVEL
Use the access code to your Fintech HR platform (IT-IRM) that you received when registering for this exercise.
Articulate the three exercises below by referring to the seminar and tutorial of the CFO modules.
1. Exercises to be done on the Fintech HR application module (IT-IRM) of your workstation:
a) Perform calculations for anticipating and mitigating operating losses from data stored in the Unexpected Losses (UL) and Expected Losses (EL) internal databases.
b) Execute financial planning based on expected losses considering the absolute VaR and the risk appetite threshold.
c) Weigh the socio-economic indicators of operational risk based on survey data provided by the HR function.
d) Distribute the economic objectives of internal financial performance to the business lines according to their consumption of budgetary resources.
e) Retrieve Fintech IT-IRM dashboard data from Excel internal reporting for quarterly, semi-annual or annual EBITDA to analyze financial performance gaps to pay variable wages.
2. Reconciliation of EC accounts with financial statements and projection of future accounts.
Proceed according to the known process
According to the accounting approach, profit-sharing represents the counterpart of performance. For example, in the context of International Accounting Standards (IAS)/International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), account(s), “Other personnel expenses” is credited. If we take the economic approach, the profit-sharing is a charge that must appear below the exceptional result. IAS/IFRS is broken down into a subdivision of account “employee incentive” and another account titled “other payroll expenses,” which is credited.
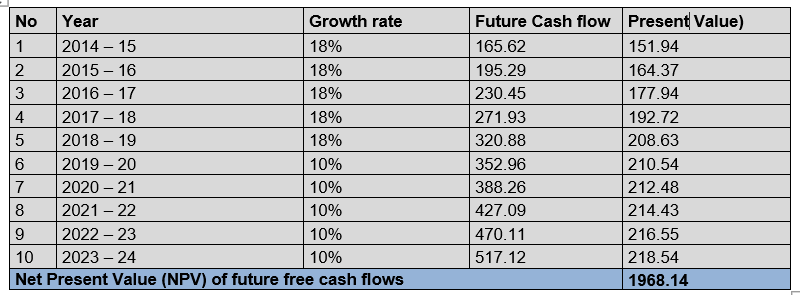
Fiscally, contrary to the provisions stipulated for participation, the amounts provisioned under the profit-sharing scheme are deductible. The incentive is subject to the social package. At the end of the fiscal year, the account “Social Security and provident contributions” is debited in IAS/IFRS and account “social organizations - other accrued liabilities” is credited. This entry is reversed on the first day of the following year (posting in reverse). With the reports from the three-year plan executed, financial analysts, including actuaries, can make projections to know the future value of the business. They can make realistic projections for the next 10 or 20 years considering historical data from the dynamics of cross-cutting interactions of the organization.
The forward-looking financial accounting process is the same as that of the usual practice below:
3. Supervision of the overall process on the basis of the standard relating to Impairment of Assets:
• IAS-IFRS 36 / Impairment of Assets. More than 100 countries use IFRS.
• For US GAAP the comparable logical process is Accounting Standards Codification (ASC) Topic 350, Intangibles — Goodwill and Other.
The interest of IAS 36, Impairment of Assets, to codify the logical sequence of non-GAAP reporting, from the collection of data from socio-economic indicators of operational risk loss to the analysis of differences, comes from the fact that IAS 36 seeks to ensure that an entity's assets are not carried at more than their recoverable amount (i.e. the higher of fair value less costs of disposal and value in use). With the exception of goodwill and certain intangible assets for which an annual impairment test is required, entities are required to conduct impairment tests where there is an indication of impairment of an asset, and the test may be conducted for a ‘cash-generating unit’ where an asset does not generate cash inflows that are largely independent of those from other assets.
The socio-economic indicators allow the non-GAAP reporting for Human Capital management accounts to run in the same logic by adapting and integrating the basic processes of IAS 36:
(a) Impairment loss: the amount by which the carrying amount of an asset or cash-generating unit exceeds its recoverable amount.
(b) Carrying amount: the amount at which an asset is recognized in the balance sheet after deducting accumulated depreciation and accumulated impairment losses.
(c) Fair value : the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date (in non-GAAP , the Fair Value Measurement reference for Human Capital Accounts Reporting is a greater ROI expected from fixed salaries and an increase in free cash flow expected from variable salaries).
(d) Identifying an asset that may be impaired:
At the end of each reporting period, an entity is required to assess whether there is any indication that an asset may be impaired (i.e. its carrying amount may be higher than its recoverable amount). IAS 36 has a list of external and internal indicators of impairment. If there is an indication that an asset may be impaired, then the asset’s recoverable amount must be calculated. [IAS 36.9].
In non-GAAP the process is the absolute OpRisk formula (VaR = EL + UL) used to calculate the economic capital (EC). For banks the EC is defined 99.95% (VaR – Expected Loss or the Risk Appetite Threshold); for Insurance companies 95.5 % and the same EC rate for insurance risk counterparty companies. Given the ORSA (Own Risk and Solvency Assessment) and countries laws deriving from the Basel III agreement they must align their risk appetite threshold with that of the insurer:
- Institutions consider all the relevant information for the affectation of credit lines to the various debtors’ categories.
- This information should be current and allow them to forecast the future performance of the exposure (Article171-2. Basel III / EU legislative acts No. 575/2013).
(e) Indications of impairment:
Indicators of Impairment are obsolescence due to new technological changes, decline in performance i.e. net cash flows of the asset or cash generating units (CGU), decline in market value of the asset, changes in economy such as an increase in labor cost, raw materials, etc. that would shrink the net cash flows of the asset.
In non-GAAP human capital reporting, indicators of impairment are on three operational risk axes:
The axis of socio-economic indicators available to all employees,
The focus of key areas for improving working conditions and
The psychosocial risks axis.
(*) Note that axis 1 (socio-economic indicators) use the internal dashboard to take immediate and effective action to address risk on the basis of six key domains of socioeconomic improvement: working conditions, organization of work, consultation, communication, coordination (3C), integrated training, working time management and strategic implementation.
(f) External sources (in non-GAAP the forward-looking approach begins with the analysis of published income statements, especially on the stock market).
(g) Internal sources (in non-GAAP the reference is corporate functions, business units, Risks register, and Socio-economic indicators).
(h) Determining recoverable amount (in non-GAAP the reference is: Potential Recoverable Loss).
(i) Value in use (in non-GAAP the reference is cash flow projections and reporting of periodic results in free cash flow).

